Did you know that every year, many people around the world lose their lives due to hepatitis? This silent disease can creep into our lives without us realizing it. The virus can damage our liver cells rapidly, and if left untreated, it can lead to cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even death. This makes it essential for us all to be aware of the dangers of this disease and take measures to protect ourselves.
What is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver caused by a viral infection. There are five main types of hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. The most concerning are hepatitis B and C, as these can lead to chronic diseases like cirrhosis and ultimately liver cancer.
What Causes Hepatitis?
Hepatitis can be caused by different viruses, some of which may not show symptoms but can still spread the virus to others. This is known as being a “carrier.” Because carriers do not show symptoms, we may unknowingly be exposed to the virus. The causes and modes of transmission for each type of hepatitis virus are as follows:
- Hepatitis A and E are transmitted through contaminated food and water. This can occur from eating raw or undercooked food or drinking unclean water. Contact with the stool of an infected person is another cause.
- Hepatitis B and C are transmitted through blood, such as sharing needles, receiving contaminated blood, or engaging in unprotected sex. Additionally, transmission can occur from mother to child during childbirth.
What Are the Symptoms of Hepatitis?
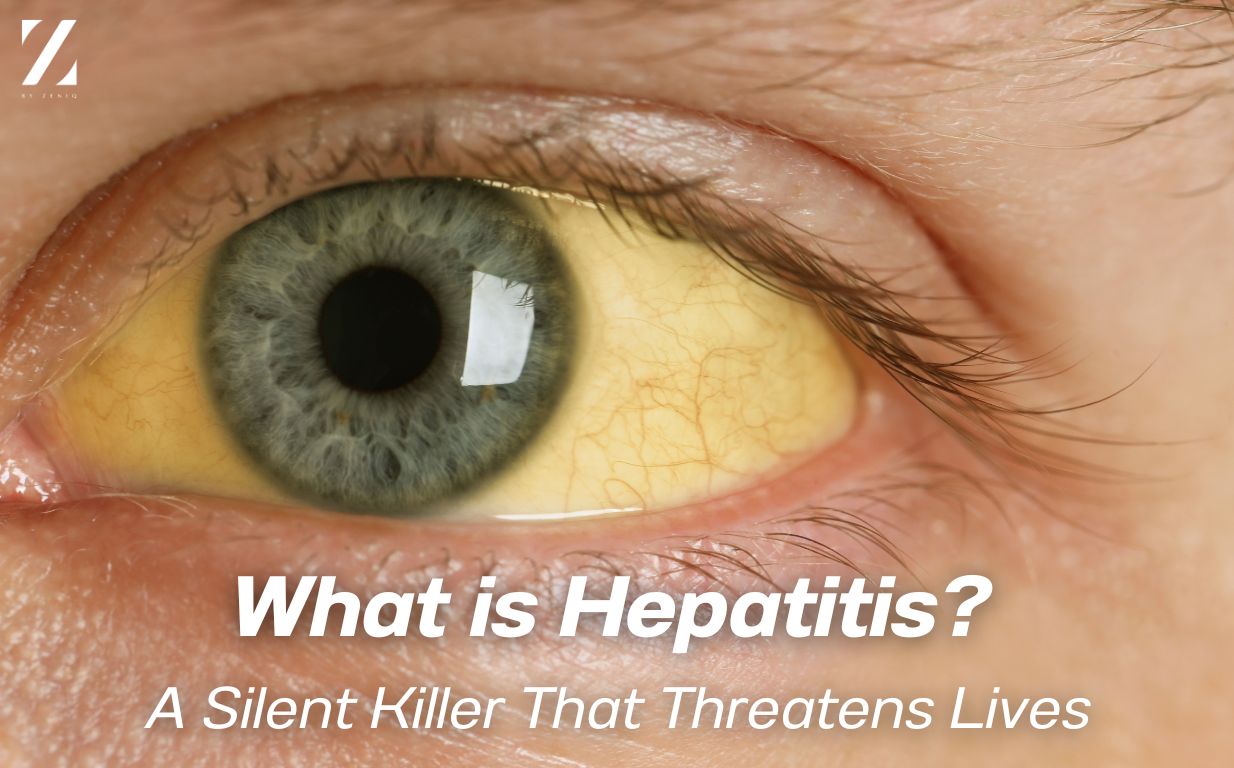
If you feel fatigued, lose your appetite, or notice yellowing of the skin or eyes, these could be warning signs of acute hepatitis. Acute hepatitis is caused by various types of viruses and often presents similar symptoms. Common signs include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Abdominal pain, often in the upper right side of the abdomen
- Nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite
- Muscle aches and body pain
- Dark urine
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes
The severity of the symptoms depends on the type of virus, the amount of virus exposure, and the individual’s overall health. These symptoms generally appear 1-4 weeks after exposure to the virus, and jaundice (yellowing) may gradually subside on its own.
What About Chronic Hepatitis?
Chronic hepatitis often does not show symptoms in its early stages. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications. Chronic hepatitis is usually caused by hepatitis B or C, which slowly damages the liver cells. Even if you feel fine, the virus continues to cause harm. Symptoms that may appear in some people include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Occasional nausea or vomiting
If left untreated, chronic hepatitis can progress to serious complications like cirrhosis and liver cancer. In the early stages of cirrhosis and liver cancer, symptoms may not be clear, or you might only experience mild fatigue. As the disease worsens, additional symptoms can appear, including:
- Abdominal swelling
- Swelling in the feet
- Vomiting blood
- Jaundice
Hepatitis C: A Chronic Condition to Watch Out For
Hepatitis C is particularly dangerous because, without proper treatment, it can slowly destroy liver cells and lead to serious complications, such as:
- Cirrhosis: Hardening of the liver, making it less effective.
- Liver Cancer: A tumor that forms in the liver.
Can Hepatitis Be Cured?
Whether hepatitis can be cured depends on the type and severity of the disease.
- Hepatitis A and E: These types often resolve on their own, but the severity can vary. The body develops immunity, preventing reinfection and progression to chronic hepatitis. However, pregnant women infected with hepatitis E are at a higher risk of complications, such as miscarriage or death, and require close medical supervision.
- Hepatitis B: There are two stages: acute and chronic. About 90% of people with acute hepatitis B recover completely. However, 5-10% may develop chronic hepatitis B, where the virus remains in the body, increasing the risk of complications like cirrhosis and liver cancer.
- Hepatitis C: More than 85% of people with hepatitis C develop chronic liver disease, which is harmful to the liver in the long term. Treatment outcomes depend on the type of virus and the liver condition. If untreated, the disease may progress to cirrhosis or liver cancer. For patients with cirrhosis or liver cancer, antiviral treatments may be less effective, and doctors often focus on managing these complications. The treatment plan will depend on the individual’s health status and associated risks.
How to Treat Hepatitis?
For acute hepatitis, such as hepatitis A, B, and E, the body can often heal itself. However, proper care can speed up recovery:
- Get plenty of rest to help the body fight the infection.
- Eat nutritious food, focusing on light, easy-to-digest meals, and avoid fatty or spicy foods.
- Drink plenty of clean water to help eliminate toxins.
- Avoid strenuous exercise and alcohol, which can worsen symptoms.
- Avoid acetaminophen (paracetamol) as it may harm the liver.
Self-Care Tips for Hepatitis Patients
If you have been diagnosed with hepatitis, self-care is critical to aid your recovery and reduce the risk of complications:
- Rest sufficiently to allow your body to heal.
- Eat foods rich in fiber, vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins like fish and chicken to nourish your liver.
- Drink plenty of clean water to flush out toxins.
- Avoid spicy foods, as they can exacerbate symptoms.
- Completely avoid alcohol, as it is toxic to the liver.
- Consult with your doctor before taking any medications, especially acetaminophen.
- Engage in light exercise, but consult with your doctor first.
- Manage stress, as it can weaken the immune system and worsen symptoms.
- Maintain good personal hygiene by washing hands frequently, especially before eating, after using the bathroom, or touching contaminated surfaces.
- Keep your doctor’s appointments for regular blood tests and liver function monitoring.
- Notify your doctor if you experience abnormal symptoms, such as severe abdominal pain, vomiting blood, or yellowing of the skin or eyes.
How to Prevent Hepatitis?
There are several preventive measures to protect yourself from hepatitis A, B, C, and E:
- Avoid contact with blood and bodily fluids of others, such as by refraining from tattooing, not sharing needles, and not using personal items like razors or nail clippers.
- Practice good hygiene by washing hands frequently, especially before meals or after using the restroom.
- Engage in safe sex by using condoms and limiting sexual partners.
- Healthcare workers should always wear protective gear when handling blood or bodily fluids, such as gloves and protective eyewear.
Summary
Hepatitis is a serious disease that can silently harm your health. There are several types, including A, B, C, D, and E, which can be transmitted through blood, food, and water. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications like cirrhosis or liver cancer. However, with proper self-care, a balanced diet, and regular medical follow-up, you can manage and prevent the progression of hepatitis.
If you’re concerned about hepatitis or need a liver health check-up, Z by Zeniq is here to offer diagnosis and personalized consultation with our expert medical team to ensure your health is well cared for in a safe and comprehensive manner.