Cervical cancer is a health threat that everyone must be concerned about, whether they are women or men who have sex. Because the HPV virus, which is the main cause of this type of cancer, can be transmitted to both sexes. But now we have an important weapon in prevention, which is the “HPV vaccine”. This type of vaccine not only helps prevent cervical cancer in women, but also reduces the risk of other sexually transmitted diseases caused by HPV in both women and men. Let’s understand the vaccine and the value of the HPV vaccine in this article.
What is Human Papilloma Virus?
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is a virus with many strains that can be spread through direct contact and sexual contact. Types 16 and 18 are the main cause of Cervical Cancer, accounting for 70% of cases. Types 6 and 11 are the most common cause of genital warts, accounting for 90% of cases. Additionally to cervical cancer, HPV is also associated with oral, throat, vulvar, and anal cancers.
Symptoms of HPV infection can vary depending on the type and location of infection. The most common symptom is the appearance of warts, which can appear as raised, flat, or pink bumps. They are most commonly found in the vagina, cervix, testicles, anus, groin, or groin. Other symptoms may include itching or burning in the infected area, bleeding during sex, foul-smelling and excessive vaginal discharge, irregular periods, and in rare cases, urinary tract obstruction due to large lumps.
However, the concern is that many HPV infections do not have these symptoms, which can delay detection and be dangerous.
Why Get the HPV Vaccine?
The HPV vaccine protects against HPV infections. Although the body can clear the virus itself in about 90% of cases, chronic infection can lead to abnormalities of the cervical lining in some.
Types of HPV Vaccines
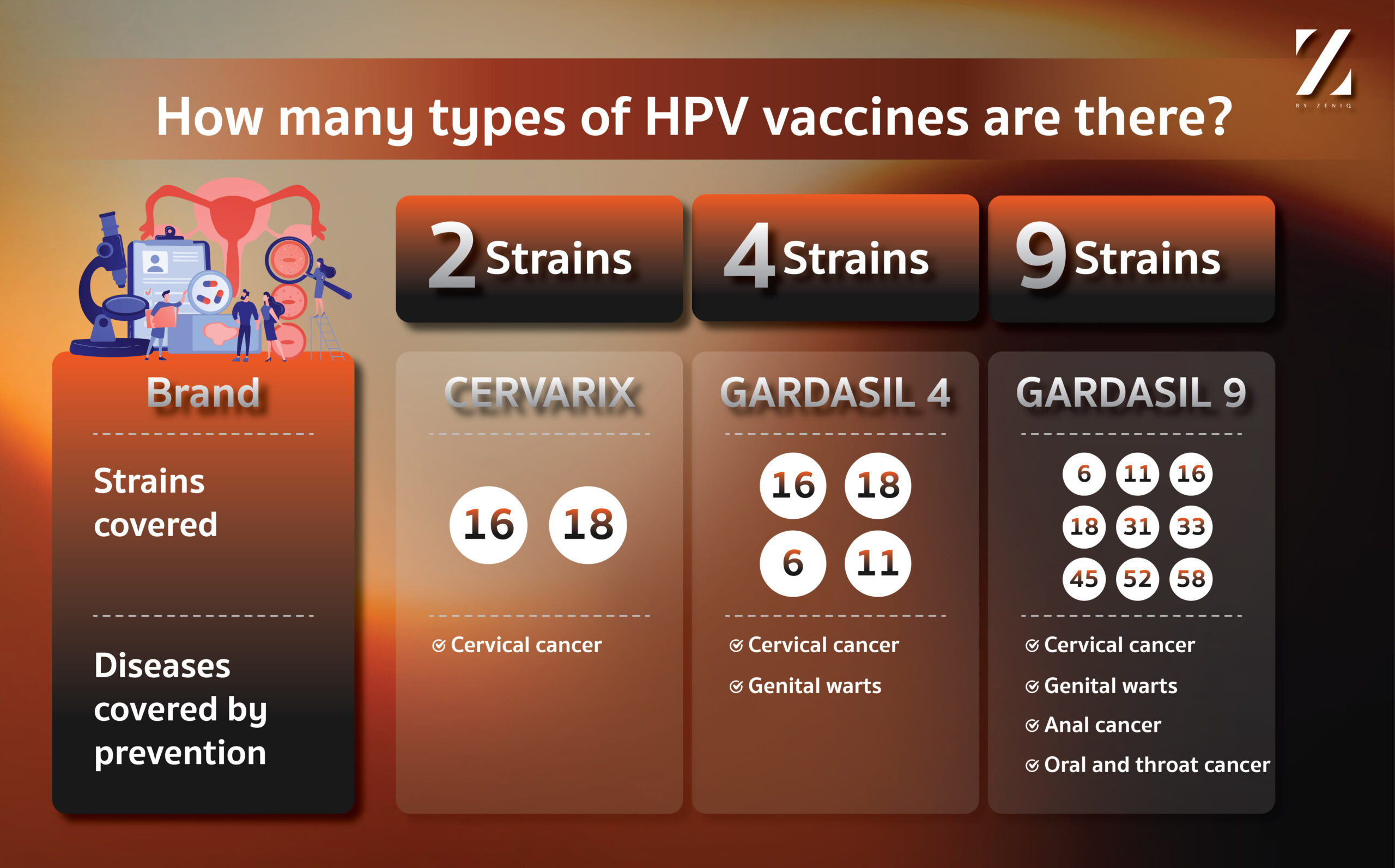
Currently, three types of HPV vaccines are available in Thailand:
- Bivalent vaccine covers types 16 and 18, which cause Cervical Cancer.
- Quadrivalent vaccine covers types 16, 18, and types 6, 11, which cause genital warts.
- Non-valent vaccine covers types 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, 58, which cause Cervical Cancer, as well as types 6 and 11, which cause genital warts. Types 16 and 18 are the most common HPV types, accounting for about 70% of Cervical Cancer-causing HPV.
It can be seen that the 2 and 4 strains of vaccine can prevent infection by about 70%, while the 9 strain vaccine can prevent another 20%, totaling about 90%.
Women Vs Men: Who Must Get HPV Vaccine?
- Both men and women aged 9-26 years need 3 injections (at 0, 1-2, and 6 months).
- Both men and women under 15 years need only 2 injections.
- People with low immunity, such as those infected with HIV, need to get 3 injections.
- Women with abnormal Cervical Cancer screening results and abnormal HPV testing results, or a history of precancerous lesions on the cervix, including a history of genital warts.
Note: Women must still get regular cervical cancer screenings.
Women and men aged 26-45 years or have had sexual intercourse, the doctor will consider injecting on a case-by-case basis.
Who is HPV Vaccines Not Recommended For?
People who are contraindicated to receive the HPV vaccine include:
- People with a history of severe allergic reactions to vaccine components
- People with yeast allergies (for Gardasil and Gardasil9 vaccines)
- Pregnant women should postpone the injection until after delivery. However, if the injection was given during pregnancy, the remaining injection can be given after delivery.
- Breastfeeding women can receive the vaccine.
How to get HPV Vaccine?
HPV vaccination must be completed as scheduled to provide the best possible immunity. Typically, a total of 3 injections are required.
- First dose: Choose an appointment date
- Second dose: 1-2 months after the first dose
- Third dose: 6 months after the first dose
For girls, if vaccination starts before age 15, only two injections may be given, spaced 6-12 months apart.
Post-injection Advice
After each vaccination, you should observe your symptoms for at least 15 minutes for safety. If you have any unusual symptoms, notify the staff immediately. For birth control, you should wait at least 1 month after receiving the full dose of vaccine to allow the vaccine to be fully effective.
Advantages of HPV Vaccines
- Effective protection against HPV: The HPV vaccine helps build immunity against the HPV, which is the main cause of Cervical Cancer, significantly reducing the risk of developing the disease.
- Very few side effects: They usually go away on their own within a few days.
- Can be used in conjunction with Cervical Cancer screening: Getting the HPV vaccine in conjunction with regular Cervical Cancer screening can help to make cervical cancer prevention more effective.
- Both men and women are protected: The HPV vaccine is not only beneficial to women, but also protects against diseases caused by HPV in men, such as genital warts and anal cancer.
Limitations of HPV Vaccines

The HPV vaccine has limitations for use in people who are hypersensitive or have a severe allergy to any component of the vaccine, such as yeast or certain preservatives. Therefore, people with a history of drug allergies should inform their doctor before receiving the vaccine.
HPV Vaccine Side Effects
- General symptoms: The most common symptoms are pain, swelling, and redness at the injection site, which should go away on their own within 2-3 days.
- Other symptoms: Low-grade fever, nausea, headache, or dizziness, which should also go away on their own.
Prevention of HPV Infection
Best way to prevent HPV infection is to follow a good lifestyle and safe practices:
- Maintain good health by exercising regularly, eating healthy, and getting enough rest.
- Practice safe sex, such as having only one partner and using condoms every time you have sex.
- Get the HPV vaccine, suitable for people aged 9-26 years.
Conclusion
HPV vaccines help protect against the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), which causes Cervical Cancer and other types of cancer. The vaccines are recommended for men, women, children and adolescents – especially before they first have sex. Although the vaccines are effective in preventing the infection, the best protection is practicing safe sex and women regularly screening for Cervical Cancer.

